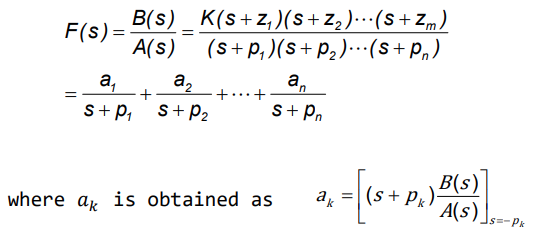[Robot sensor application] Basic concept
in Robotics / Robotics & Control on Robotics
Table of Contents
Sensor
- Device to measure the physical quantity of concern
- position, velocity, acceleration torque, temperature
- Transducer
- Device to convert from one kind of energy to another kind one.
- light energy à electrical energy
- Device to convert from one kind of energy to another kind one.
General Classification
- Active vs Passive
- Active: emit energy to environment
- More robust, less efficient
- Passive: passively receive energy from environment.
- Less intrusive, but depends on environment e.g. light for camera
- Active: emit energy to environment
- Analog vs Digital
- Contact vs Non-contact
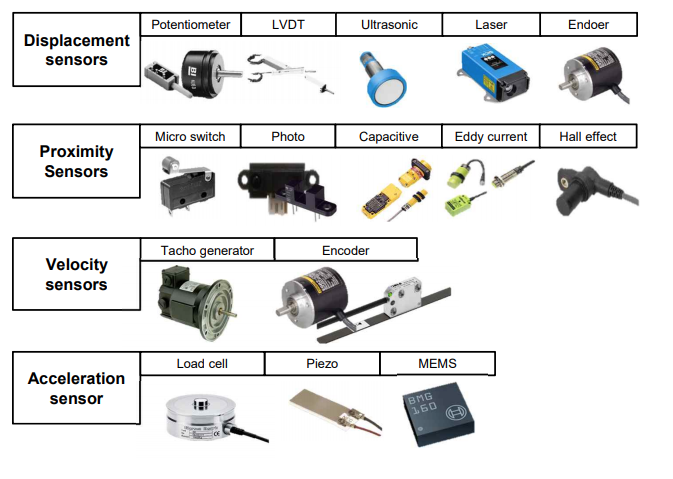
by physical quantity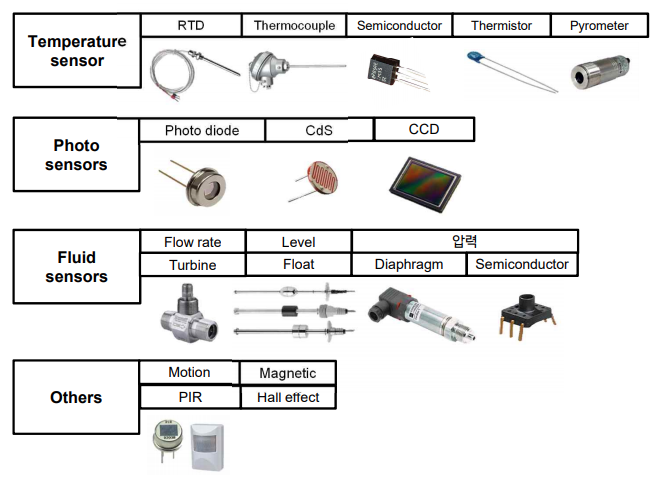
Terminology
- Range, Span
- The range of a transducer defines the limits between which the input can vary. n The span is the maximum value of the input minus the minimum value
- if a thermometer cover -40°~ +50°C, Range is -40°~ +50°C and span is 90°C.
- Error:
- measured value - true value.
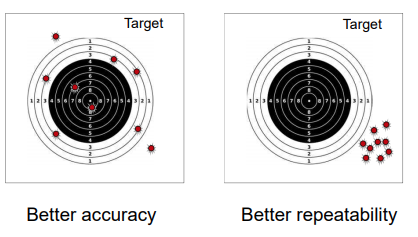
- Accuracy:
- guaranteed minimum and maximum error including all possible effects.
- accuracy ± 2
- Repeatability/Reproducibility
- ability to give the same output for repeated applications of the same input value.
- described by % of full range.
- Sensitivity
- The sensitivity is the relationship indicating how much output is produced if unit input is applied.
- dy/dx
- Linearity
- dy/dx is const for all x
- Dynamic range
- cover wide measurement range as well as detect small changes of measure. \(\rightarrow\) wide Dynamic range.
- logarithmic response \(\rightarrow\) wide dynamic range camera
- Response Time
- Time needed to result in change output after changes in input
- Resolution
- minimum input change can be recognized from output
- Bandwidth
- input frequency limit can be read 70% magnitude of dc input
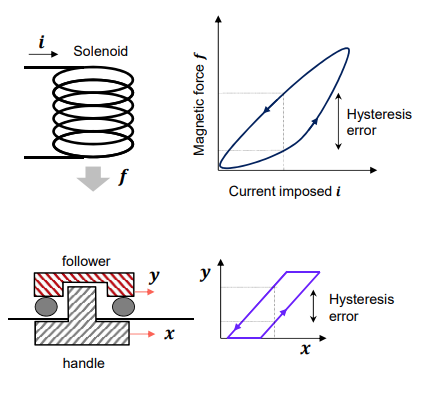
- Hysteresis error
- hystera means a psychological disorder.
- hysteresis represents exaggerated or uncontrollable errors of a device
Laplace transform
- Purpose:
- Differential Eq. in time domain \(\rightarrow\) Algebraic Eq. in complex domain
- Definition :
여기서, s는 복소변수 그리고 f(t) = 0, for t < 0
- Linearity of Laplace operator
- Superposition(homogeneity, additivity)
Why Laplace transformation?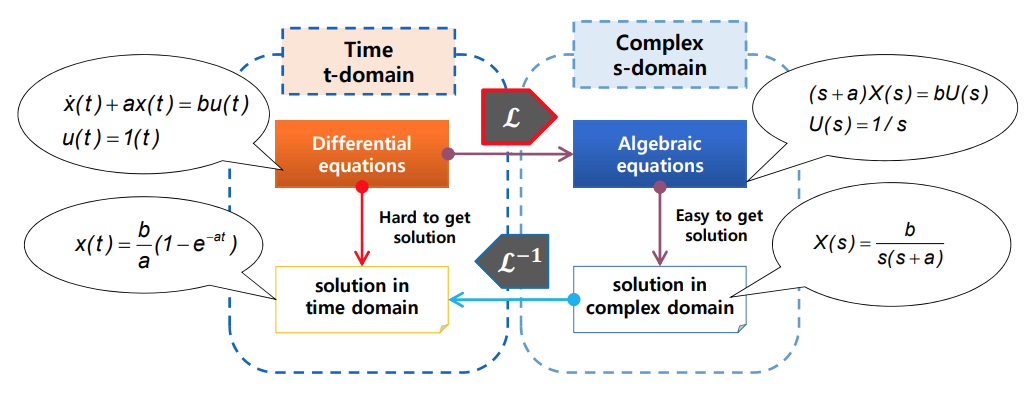
Table of Laplace Tr.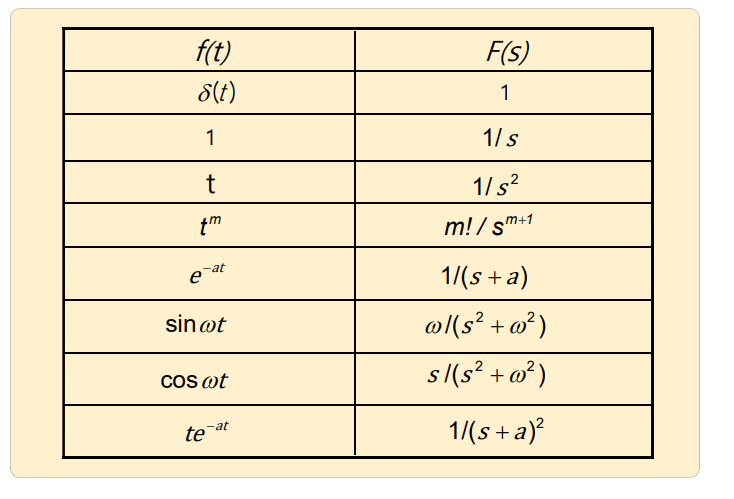
Formula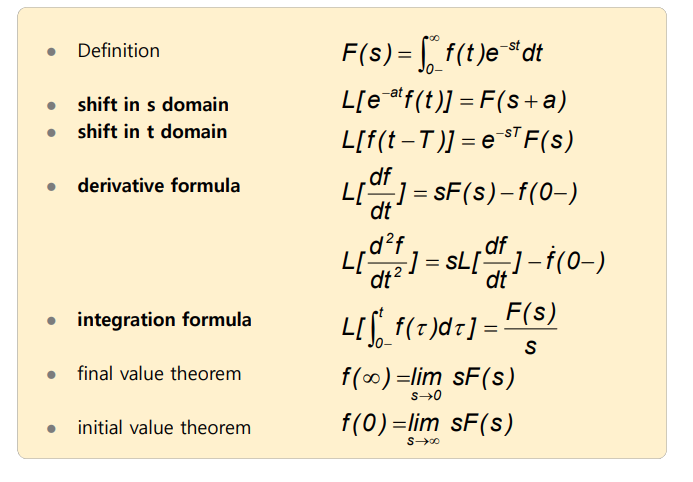
최종값 및 초기값의 정리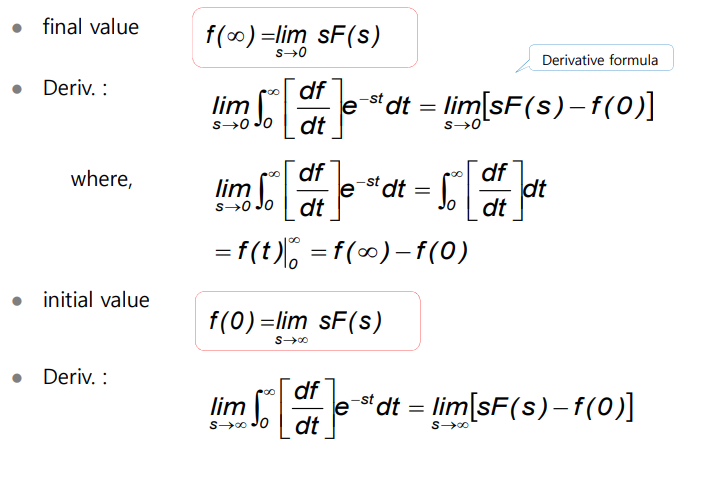
Inverse Laplace transform
- Laplace tr. \(\rightarrow\) algebraic eq.
- if solution of the algebraic eq. is F(s)
- A(s) : denominator of F(s)
- Poles: roots of polynomial A(s) = 0
- There are 3 cases in the poles of F(s)
- (1) Distinct real poles
- (2) Multiple real poles
- (3) Complex poles
- cf. Root of equation B(s)=0 are called zeros.
- Partial fraction expansion: